Meta-analysis reveals weak associations between reef fishes and corals - Nature.com
Abstract
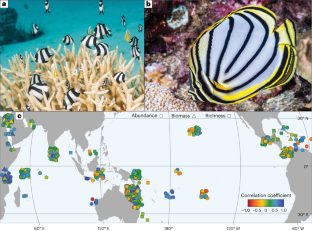
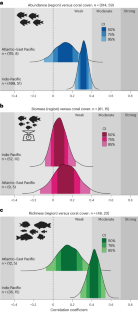
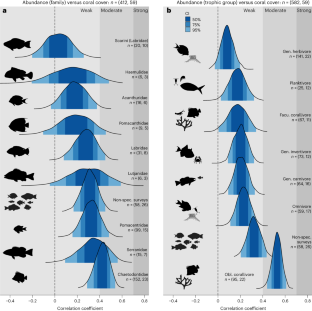
Habitat associations underpin species ecologies in high-diversity systems. Within tropical, shallow water coral reefs, the relationship between fishes and corals is arguably the most iconic and highly scrutinized. A strong relationship between fishes and reef-building hard corals is often assumed, a belief supported by studies that document the decline of reef fishes following coral loss. However, the extent of this relationship is often unclear, as evidenced by conflicting reports. Here we assess the strength of this ecological association by relying on literature that has surveyed both fishes and corals synchronously. We quantitatively synthesize 723 bivariate correlation coefficients (from 66 papers), published over 38 years, that relate fish metrics (abundance, biomass and species richness) with the percentage of hard coral cover. Remarkably, despite extensive variation, the pattern of association on a global scale reveals a predominantly positive, albeit weak (|r| < 0.4), correlation. Even for commonly hypothesized drivers of fish–coral associations, fish family and trophic group, associations were consistently weak. These findings question our assumptions regarding the strength and ubiquity of fish–coral associations, and caution against assuming a direct and omnipresent relationship between these two iconic animal groups.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during our study is available at https://doi.org/10.25903/chbr-5x77.
Code availability
The codes generated during our study is available at https://doi.org/10.25903/chbr-5x77.
References
Morrison, M. L., Marcot, B. & Mannan, W. Wildlife–Habitat Relationships: Concepts and Applications (Island Press, 2012).
MacArthur, R. H. & MacArthur, J. W. On bird species diversity. Ecology 42, 594–598 (1961).
Soto-Shoender, J. R., McCleery, R. A., Monadjem, A. & Gwinn, D. C. The importance of grass cover for mammalian diversity and habitat associations in a bush encroached savanna. Biol. Conserv. 221, 127–136 (2018).
Connell, J. H. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 199, 1302–1310 (1978).
Bellwood, D. R. & Hughes, T. P. Regional-scale assembly rules and biodiversity of coral reefs. Science 292, 1532–1534 (2001).
Komyakova, V., Munday, P. L. & Jones, G. P. Relative importance of coral cover, habitat complexity and diversity in determining the structure of reef fish communities. PLoS ONE 8, e83178 (2013).
Stoddart, D. R. Ecology and morphology of recent coral reefs. Biol. Rev. 44, 433–498 (1969).
Cheal, A. J. et al. Responses of coral and fish assemblages to a severe but short-lived tropical cyclone on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 21, 131–142 (2002).
Hughes, T. P. Catastrophes, phase shifts, and large-scale degradation of a Caribbean coral reef. Science 265, 1547–1551 (1994).
Jones, G. P. & Syms, G. Disturbance, habitat structure and the ecology of fishes on coral reefs. Aust. J. Ecol. 23, 287–297 (1998).
Coker, D. J., Wilson, S. K. & Pratchett, M. S. Importance of live coral habitat for reef fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 24, 89–126 (2014).
Cole, A. J., Pratchett, M. S. & Jones, G. P. Diversity and functional importance of coral-feeding fishes on tropical coral reefs. Fish Fish. 9, 286–307 (2008).
Russ, G. R., Rizzari, J. R., Abesamis, R. A. & Alcala, A. C. Coral cover a stronger driver of reef fish trophic biomass than fishing. Ecol. Appl. 31, e02224 (2021).
Bell, J. & Galzin, R. Influence of live coral cover on coral-reef fish communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 15, 265–274 (1984).
Booth, D. J. & Beretta, G. A. Changes in a fish assemblage after a coral bleaching event. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 245, 205–212 (2002).
Jones, G. P., McCormick, M. I., Srinivasan, M. & Eagle, J. V. Coral decline threatens fish biodiversity in marine reserves. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 8251–8253 (2004).
Wilson, S. K., Graham, N. A. J., Pratchett, M. S., Jones, G. P. & Polunin, N. V. C. Multiple disturbances and the global degradation of coral reefs: are reef fishes at risk or resilient? Global Change Biol. 12, 2220–2234 (2006).
Pratchett, M. S., Hoey, A. S., Wilson, S. K., Messmer, V. & Graham, N. A. J. Changes in biodiversity and functioning of reef fish assemblages following coral bleaching and coral loss. Diversity 3, 424–452 (2011).
Ceccarelli, D. M., Emslie, M. J. & Richards, Z. T. Post-disturbance stability of fish assemblages measured at coarse taxonomic resolution masks change at finer scales. PLoS ONE 11, e0156232 (2016).
Yan, H. F. & Bellwood, D. R. Multi-decadal stability of fish productivity despite increasing coral reef degradation. Funct. Ecol. 37, 1245–1255 (2023).
Friedlander, A. M. & Parrish, J. D. Habitat characteristics affecting fish assemblages on a Hawaiian coral reef. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 224, 1–30 (1998).
Wismer, S., Tebbett, S. B., Streit, R. P. & Bellwood, D. R. Spatial mismatch in fish and coral loss following 2016 mass coral bleaching. Sci. Total Environ. 650, 1487–1498 (2019).
Wismer, S., Tebbett, S. B., Streit, R. P. & Bellwood, D. R. Young fishes persist despite coral loss on the Great Barrier Reef. Commun. Biol. 2, 1–7, 456 (2019).
Wilson, S. K. et al. Habitat utilization by coral reef fish: implications for specialists vs. generalists in a changing environment. J. Anim. Ecol. 77, 220–228 (2008).
Siqueira, A. C., Muruga, P. & Bellwood, D. R. On the evolution of fish–coral interactions. Ecol. Lett. 26, 1348–1358 (2023).
Pratchett, M. S. et al. in Oceanography and Marine Biology Vol. 46, 251–296 (CRC Press, 2008).
Munday, P. L., Jones, G. P., Pratchett, M. S. & Williams, A. J. Climate change and the future for coral reef fishes. Fish Fish. 9, 261–285 (2008).
Strona, G. et al. Global tropical reef fish richness could decline by around half if corals are lost. Proc. Biol. Sci. 288, 20210274 (2021).
Gurevitch, J., Koricheva, J., Nakagawa, S. & Stewart, G. Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis. Nature 555, 175–182 (2018).
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V, Higgins, J. P. T. & Rothstein, H. R. Introduction to Meta-analysis (John Wiley & Sons, 2009).
Nakagawa, S. & Cuthill, I. C. Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 82, 591–605 (2007).
Schober, P. & Schwarte, L. A. Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 126, 1763–1768 (2018).
Bejarano, I. & Appeldoorn, R. S. Seawater turbidity and fish communities on coral reefs of Puerto Rico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 474, 217–226 (2013).
Benfield, S., Baxter, L., Guzman, H. M. & Mair, J. M. A comparison of coral reef and coral community fish assemblages in Pacific Panama and environmental factors governing their structure. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 88, 1331–1341 (2008).
Boaden, A. E. & Kingsford, M. J. Predators drive community structure in coral reef fish assemblages. Ecosphere 6, 1–33 (2015).
Bouchon-Navaro, Y. & Bouchon, C. Correlations between chaetodontid fishes and coral communities of the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea). Environ. Biol. Fishes 25, 47–60 (1989).
Brewer, T. D., Cinner, J. E., Green, A. & Pandolfi, J. M. Thresholds and multiple scale interaction of environment, resource use, and market proximity on reef fishery resources in the Solomon Islands. Biol. Conserv. 142, 1797–1807 (2009).
Burt, J. A. et al. Biogeographic patterns of reef fish community structure in the northeastern Arabian Peninsula. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 68, 1875–1883 (2011).
Campbell, S. J. et al. Avoiding conflicts and protecting coral reefs: customary management benefits marine habitats and fish biomass. Oryx 46, 486–494 (2012).
Chung, F. C., Komilus, C. F. & Mustafa, S. Effect of the creation of a marine protected area on populations of Coral Trout in the coral triangle region. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 10, 1–9 (2017).
Cox, C., Valdivia, A., McField, M., Castillo, K. & Bruno, J. F. Establishment of marine protected areas alone does not restore coral reef communities in Belize. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 563, 65–79 (2017).
Crosby, M. P. & Reese, E. S. Relationship of habitat stability and intra-specific population dynamics of an obligate corallivore butterflyfish. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 15, 13–25 (2005).
Dominici-Arosemena, A. & Wolff, M. Reef fish community structure in the Tropical Eastern Pacific (Panamá): living on a relatively stable rocky reef environment. Helgol. Mar. Res. 60, 287–305 (2006).
Emslie, M. J., Pratchett, M. S., Cheal, A. J. & Osborne, K. Great Barrier Reef butterflyfish community structure: the role of shelf position and benthic community type. Coral Reefs 29, 705–715 (2010).
Emslie, M. J. et al. Regional-scale variation in the distribution and abundance of farming damselfishes on Australia's Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Biol. 159, 1293–1304 (2012).
Epstein, H. E. & Kingsford, M. J. Are soft coral habitats unfavourable? A closer look at the association between reef fishes and their habitat. Environ. Biol. Fishes 102, 479–497 (2019).
Espinosa-Andrade, N., Suchley, A., Reyes-Bonilla, H. & Alvarez-Filip, L. The no-take zone network of the Mexican Caribbean: assessing design and management for the protection of coral reef fish communities. Biodivers. Conserv. 29, 2069–2087 (2020).
Feary, D. A. et al. Fish communities on the world's warmest reefs: what can they tell us about the effects of climate change in the future? J. Fish Biol. 77, 1931–1947 (2010).
Feeney, W. E. et al. Long term relationship between farming damselfish, predators, competitors and benthic habitat on coral reefs of Moorea Island. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–8, 14548 (2021).
Galbraith, G. F., Cresswell, B. J., McCormick, M. I., Bridge, T. C. & Jones, G. P. High diversity, abundance and distinct fish assemblages on submerged coral reef pinnacles compared to shallow emergent reefs. Coral Reefs 40, 335–354 (2021).
Garpe, K. C. & Öhman, M. C. Non-random habitat use by coral reef fish recruits in Mafia Island Marine Park, Tanzania. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 29, 187–199 (2007).
Garpe, K. C. & Öhman, M. C. Coral and fish distribution patterns in Mafia Island Marine Park, Tanzania: fish–habitat interactions. Hydrobiologia 498, 191–211 (2003).
Glynn, P. W., Enochs, I. C., Afflerbach, J. A., Brandtneris, V. W. & Serafy, J. E. Eastern Pacific reef fish responses to coral recovery following El Niño disturbances. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 495, 233–247 (2014).
Graham, N. A. J., Wilson, S. K., Pratchett, M. S., Polunin, N. V. C. & Spalding, M. D. Coral mortality versus structural collapse as drivers of corallivorous butterflyfish decline. Biodivers. Conserv. 18, 3325–3336 (2009).
Harborne, A. R...
Comments
Post a Comment